Techne: Tools
Essential Items estimator tool
To gauge the need for essential items requirements during the COVID-19 pandemic, WHO has developed a suite of complimentary surge excel calculators – supplies, drugs, WASH and logistic, personal protective equipment and biomedical devices. All calculators rely on data collected from the fields and expert’s contributions.
Despite the variety of tools available, forecasting the needs to open and run a treatment center is still challenging due to several limitations of the existing tools including their complexity and accessibility.
This online tool centralizes the different functionalities to ensure a more effective, user friendly and rational use. It provides an estimation of the essential items needed to open and/or manage a treatment center according to few inputs provided by users such number of beds, average length of hospitalisation and period considered. As of today, the tool covers two diseases, Ebola Virus Diseases and COVID-19 and should be available online, offline and on different devices such as laptops and smartphones.
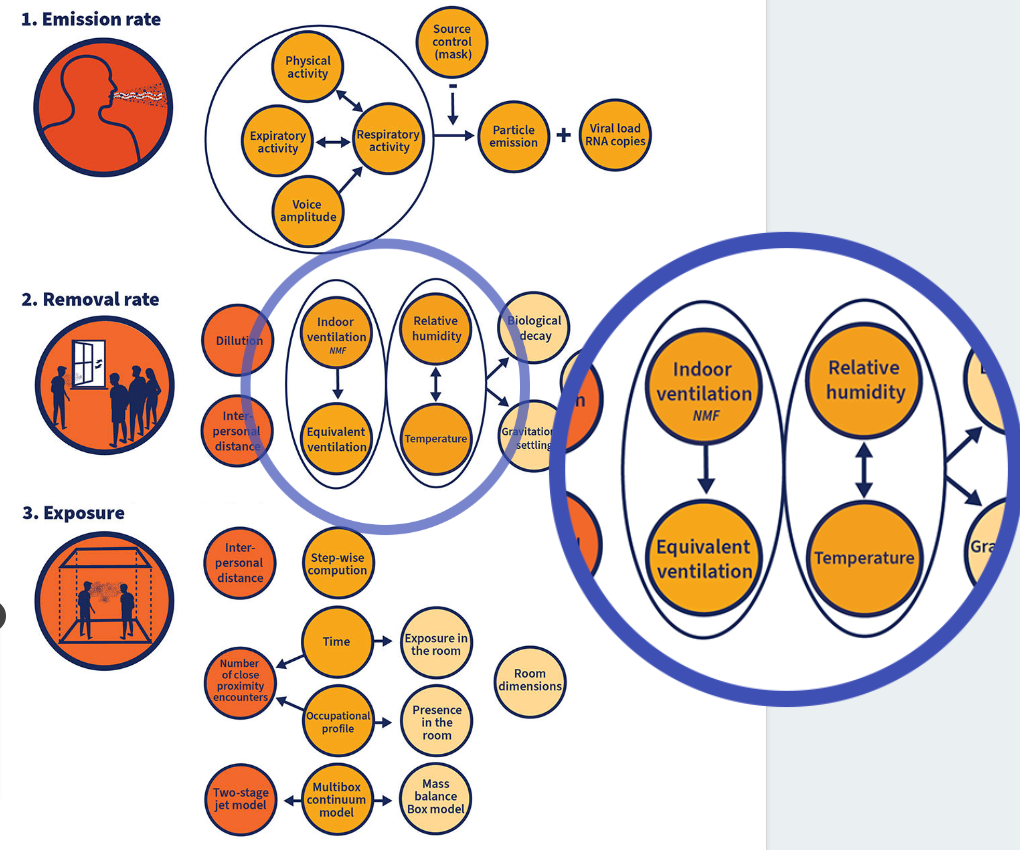
Airborn Risk Assessment Tool
Over the past several months several quantitative tools have been developed by various scientists and engineers to model the SARS-CoV-2 infection risk associated with indoor occupancy during the pandemic. While these tools all incorporate ventilation as a primary control measure, they differ in their inclusion of epidemiological/virological aspects and variables, how emission sources are represented, and how the risk is assessed, based on a time-dependent exposure to infectious aerosols. They also differ in terms of their platform, target users, and overall degree of technical complexity. For these tools to be widely used and to be able to inform policy and/or induce an update in the regulatory framework, they must be applicable to a diverse building typology, be validated by real world epidemiological studies, and apply the most up-to-date scientific knowledge of aerosol science and host-pathogen interaction. They must also be easy to use and understand, contributing towards a broader knowledge of “airborne transmission” and improved scientific consensus surrounding its importance in public, residential and health care settings.
ARIA, the online tool to estimate SARS-CoV-2 airborne transmission in indoor settings has been developed through a human centred design approach. The interactive system developed aims to provide an interface focusing on the users, their needs, and requirements, as well as applying common application-based standards, ergonomics, and usability techniques for calculating both short- and long-range transmission. In the future, an extension of the new tool to other pathogens beyond SARS-CoV-2 could be considered.
Health Emergency Facility Tool
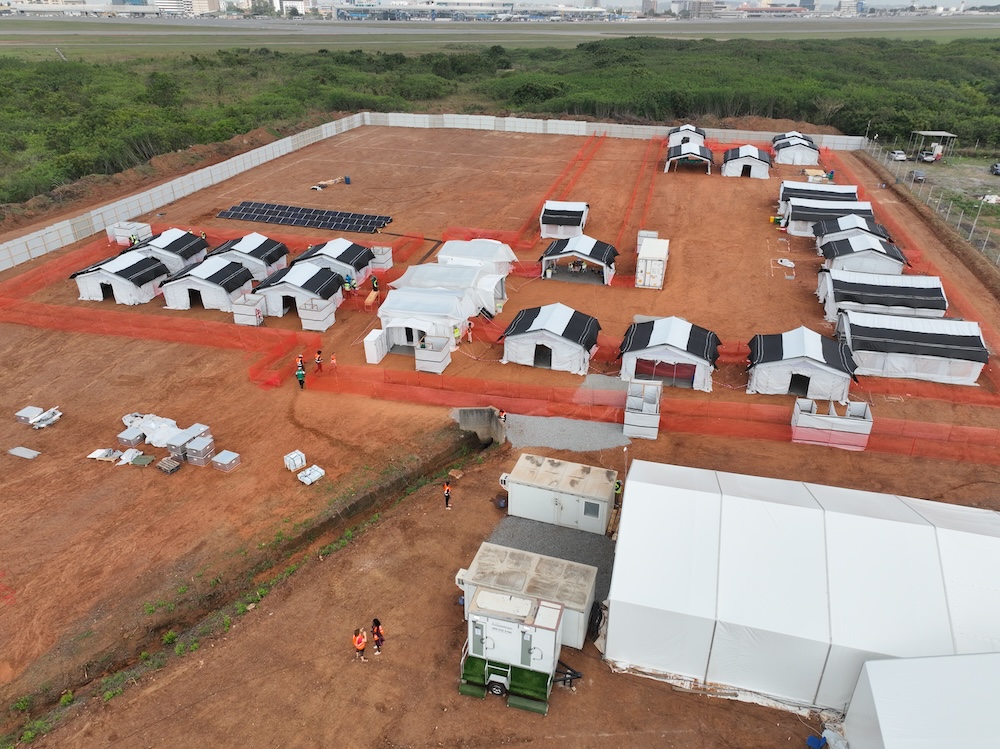
The recent challenges of conflicts, natural hazards, and disease outbreaks like Ebola, Marburg, Cholera, and COVID-19 have frequently overwhelmed health care systems, emphasizing the urgent need for rapidly deployable health facilities. Many ad-hoc facilities set up in response to such emergencies take months to develop, with coordination across stakeholders hindered by differing priorities, protocols, and resources.
To address this, WHO, UNICEF, and MSF, through WHO-Techne, developed the Health Emergency Facility (HEF) digital tool. Building on the Essential Items Estimator, the HEF is a multiagency tool designed to provide rapidly deployable, family-friendly health responses during outbreaks. These standardized facilities can be operational within days, saving critical time by streamlining planning, procurement, and design processes.
By leveraging the technical expertise, innovation, and resources of each organization, the HEF tool enables emergency planners to quickly configure and customize robust health facilities suited to specific emergencies. Using context-specific inputs, the tool generates layouts and editable procurement lists, covering all components from structure, water and power supply to medical equipment and medicines.
The HEF's primary impact is speed and efficiency, helping prevent health systems from being overwhelmed while maintaining quality care. As epidemics become more frequent and widespread, the HEF tool supports the preparedness and response to future health crises.