Module 3
Tackling the social determinants of health and workers’ and occupational health and safety
Overview
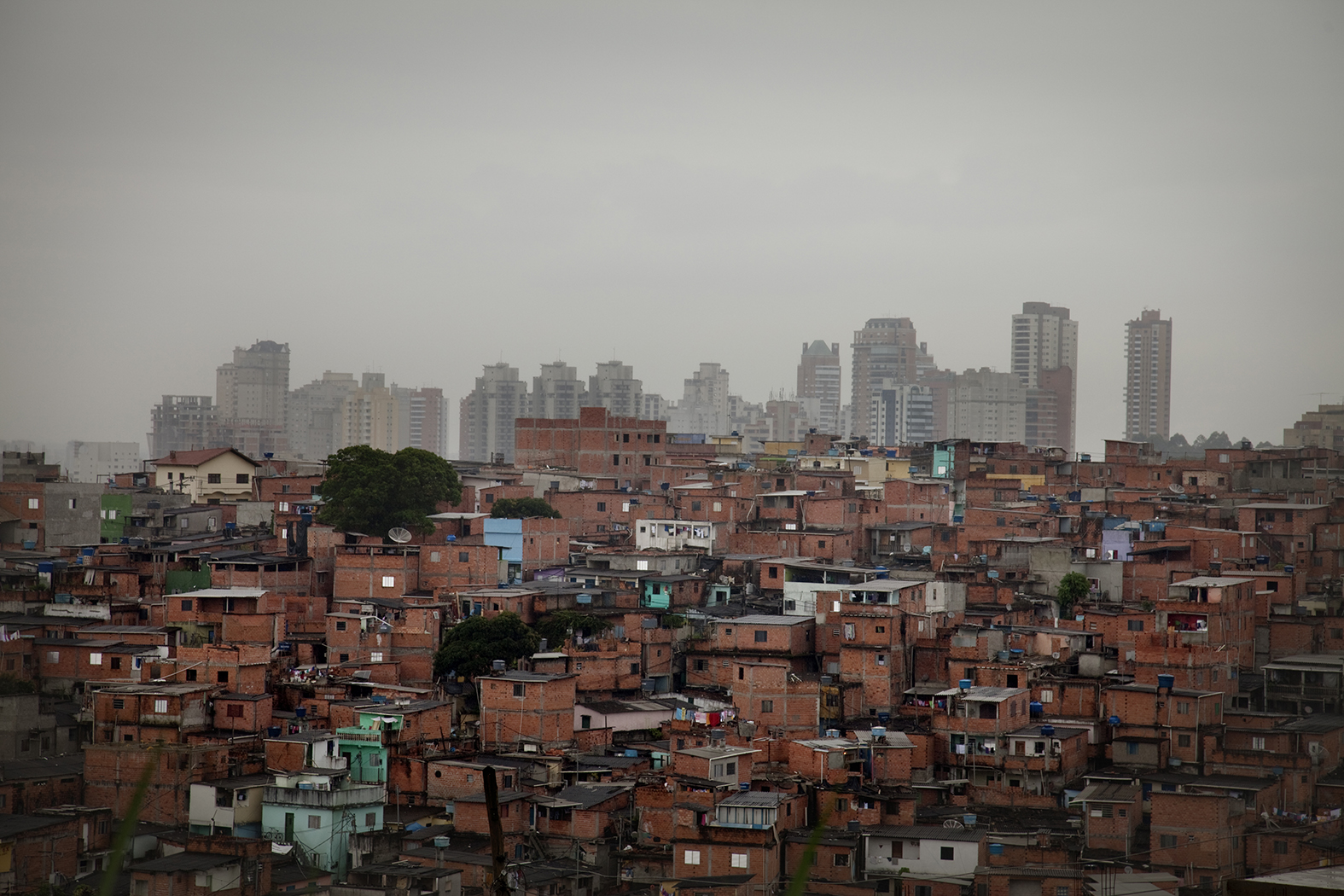
The social determinants of health are the nonmedical factors that influence health outcomes. They are the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live and age: living and working conditions; general socioeconomic, cultural and environmental conditions; and the accessibility, acceptability and quality of services. There are also a wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life, including economic policies and systems, development agendas, social norms, social policies and political systems. These determinants, which can change over time, are largely responsible for health inequalities and inequities within and between countries.
Inequalities in health and access to quality care for refugees and migrants cannot be addressed by health systems alone. Social determinants of health such as education, employment, social security and housing will all also have a considerable impact on health. Migration or displacement can also be a determinant of health in itself and can put at risk the physical, mental and social well-being of refugees and migrants, particularly those fleeing involuntarily from natural or human-created disasters.
The module contains the following four tools.Actions to be considered
- Implement guidance and assessment tools and elaborate country-specific fact sheets and standards in order to highlight and respond to social and economic factors relevant to refugee and migrant health, in the context of universal health coverage (UHC) and the SDGs and in close collaboration with the International Organization for Migration, the International Labour Organization (ILO) and the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees.
- Identify relevant sectors and stakeholders that contribute to tackling social determinants of refugee and migrant health and identify specific areas for dialogue and joint actions on achieving UHC.
- Train all personnel working with refugees and migrants on the social determinants of health and necessary policy responses and professional training for health workers.
- Ensure that health planners and health-care workers are offered support and knowledge-sharing opportunities in order to implement appropriate refugee- and migrant-sensitive health interventions that also provide affordable and equitable access to all people.
- Support the development of national action plans and policies, and strengthen institutional capacities for promoting the health of refugee and migrant workers and their families at international forums and in instruments for collaboration and mechanisms of social protection, including the development of tools, policy options, indicators and information materials in line with the provisions of the Sixtieth World Health Assembly resolution WHA60.26 on workers' health.